In the rapidly evolving world of technology, small business owners are increasingly hearing about Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Large Language Models (LLMs). While these terms are often used interchangeably, they represent different concepts with unique applications for small businesses. This article aims to clarify the distinction between LLMs and AI, using relevant examples to illustrate their roles in the small business ecosystem.
What is Artificial Intelligence (AI)?
Artificial Intelligence is a broad field of computer science focused on creating smart machines capable of performing tasks that typically require human intelligence. AI encompasses various subfields, including machine learning, natural language processing, computer vision, and robotics.
What are Large Language Models (LLMs)?
Large Language Models are a specific type of AI system designed to understand, generate, and manipulate human language. They are trained on vast amounts of text data and can perform various language-related tasks.
Key Differences Between AI and LLMs
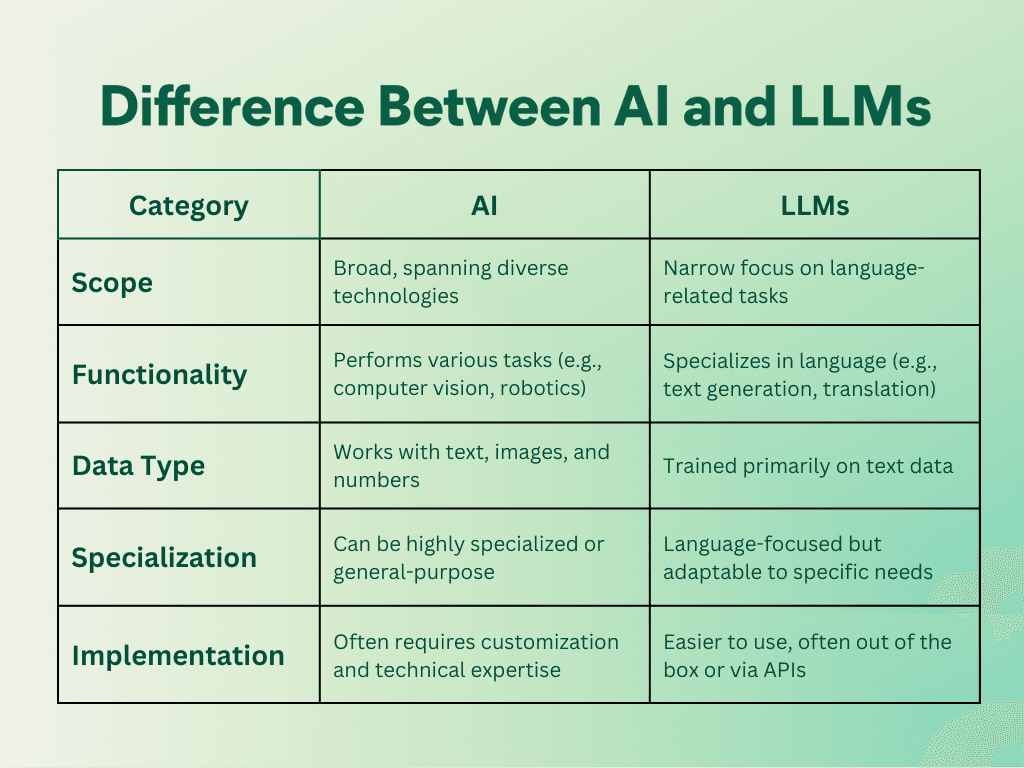
Scope:
AI is a broad field encompassing various technologies and approaches while LLMs are a specific application of AI focused on language processing and generation.
Small business example: An AI system might manage entire business processes, like inventory management, while an LLM might be used specifically for generating product descriptions within that system.
Functionality:
AI can be designed for a wide range of tasks, from visual recognition to decision-making, while LLMs specialize in language-related tasks such as translation, summarization, and text generation.
Small business example: An AI-powered point-of-sale system might use computer vision to recognize products and process transactions, while an LLM could be used to generate personalized receipts or follow-up emails.
Data Requirements:
AI systems can be trained on various types of data, including images, numbers, and text, while LLMs primarily require large amounts of text data for training.
Small business example: An AI system for predictive maintenance might use sensor data from equipment, while an LLM for customer support would be trained on previous customer interactions and product documentation.
Specialization:
AI systems can be highly specialized for specific tasks or more general-purpose, while LLMs are inherently focused on language tasks but can be fine-tuned for specific applications.
Small business example: A specialized AI might be used for facial recognition in a small retail store's security system, while an LLM could be employed across multiple departments for tasks like email drafting, report summarization, and customer query responses.
Implementation:
Implementing AI often requires significant customization and technical expertise, while LLMs can often be used "out of the box" or with minimal fine-tuning, making them more accessible for small businesses.
Small business example: Developing a custom AI system for financial forecasting might require a team of data scientists, while using an LLM for generating financial report summaries could be as simple as integrating with an existing API.
How Small Businesses Can Maximise Their Productivity Using Both AI and LLMs
Customer Service:
- AI: Implement a smart chatbot that can handle basic queries and route complex issues.
- LLM: Use to generate human-like responses for more nuanced customer interactions.
Marketing:
- AI: Utilize predictive analytics to target advertising and optimize marketing spend.
- LLM: Generate engaging marketing copy and personalized email campaigns.
Operations:
- AI: Employ computer vision for quality control in manufacturing or food preparation.
- LLM: Create and update standard operating procedures and employee handbooks.
Financial Management:
- AI: Use machine learning algorithms for fraud detection and risk assessment.
- LLM: Automatically extract and categorize data from receipts, simplifying expense tracking and bookkeeping with apps like Receiptor AI. Generate easy-to-understand summaries of financial reports for stakeholders.
Product Development:
- AI: Analyze customer data to identify trends and inform product improvements.
- LLM: Assist in creating detailed product specifications and user manuals.
Conclusion
While AI and LLMs are related concepts, understanding their differences can help small business owners make informed decisions about which technologies to adopt. AI offers a broad range of capabilities that can transform various aspects of business operations, while LLMs provide powerful tools for language-related tasks that can enhance communication, content creation, and information processing.
As these technologies continue to evolve, small businesses that strategically implement both AI and LLMs will be well-positioned to improve efficiency, enhance customer experiences, and gain a competitive edge in their respective markets.
