TL;DR: Is private school tuition a tax deductible in the US?
Here's how it works:
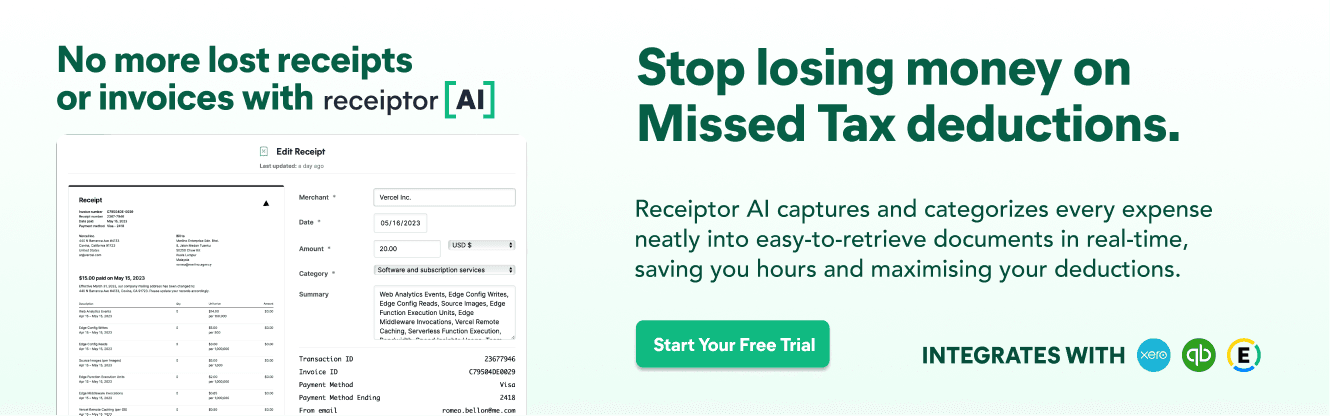
Private school tuition isn’t federally deductible unless it’s medically necessary and prescribed by a doctor. If eligible, report it on Schedule A and only deduct amounts exceeding 7.5% of AGI. Common mistakes include assuming general deductibility, lacking documentation, not itemizing, or missing state-specific tax benefits.
Understanding how to claim private school tuition as a tax deductible in the US can lead to significant tax savings. We strongly suggest you consult with a tax professional to ensure you're maximizing your eligible deductions and complying with current tax laws in the US.
Here is a summary table:
Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
Who can claim private school tuition in the US? | Children with special needs, private school recommended by physicians, or schools that provide specialized education |
Where to report on tax return | Schedule A (Form 1040) |
Requirements | Physician statement, payment receipts, school curriculum records |
Who can claim private school tuition as a tax deduction?
Only a few situations allow for a deduction: if the child has special needs, if a physician formally recommends the private school for medical or developmental reasons, and if the school provides specialized education. Additionally, certain state tax codes may allow partial deductions or credits for private school tuition, so it’s important to check with your state tax authority.
Where do I report private school tuition on my tax return?
If eligible, you would need to itemize deductions and report the tuition as a medical expense on Schedule A (Form 1040). However, you can only deduct the portion of qualified medical expenses that exceed 7.5% of your adjusted gross income (AGI).
What documentation do I need to claim private school tuition as a tax deductible?
You’ll need a physician’s statement recommending the school for medical reasons, payment receipts for tuition and related costs, and records showing the school’s curriculum and services align with your child’s medical or developmental needs.
What are common mistakes or misconceptions about claiming private school tuition as a tax deductible?
Many people mistakenly believe that all private school tuition is deductible, try to deduct it without a medical justification, forget to itemize when required, or ignore state-level tax benefits that may allow for partial relief.
Tax Deductibles 101
What defines a tax deductible?
A tax-deductible expense is one that reduces your taxable income, lowering the tax you owe. Common examples include business costs, mortgage interest, and charitable donations. You can claim a standard deduction or itemise if your expenses are higher.
Common tax-deductible expenses
Personal | Business |
|---|---|
Mortgage interest payments | Office rent and utilities |
Charitable donations | Employee salaries and benefits |
Medical and dental expenses exceeding a certain percentage of income | Business travel and meals |
State and local taxes (with limitations) | Advertising and marketing costs |
Student loan interest | Professional services (e.g., legal and accounting fees) |
Tax Deduction vs. Tax Credit
It's important to distinguish between a tax deduction and a tax credit:
Tax Deduction | Tax Credit | |
|---|---|---|
Difference | Reduces your taxable income. The actual tax savings depend on your marginal tax rate. | Directly reduces your tax liability pound-for-pound. |
Example | A £1,000 deduction in a 20% tax bracket saves you £200. | A £1,000 tax credit lowers your tax bill by £1,000, regardless of your tax bracket. |
How to manage your tax deductibles like a pro
1. Keep detailed records
It’s way easier to stay on top of your taxes if you’re not hunting for crumpled receipts at the last minute. Start saving invoices, receipts, and notes on business expenses throughout the year, not just when April rolls around.
If it helps, use an app to scan documents as you go to keep things tidy and searchable. The more organized you are, the more likely you’ll catch deductions you’d otherwise miss. And come tax time? You’ll thank yourself.
You may like this: What deductions can I claim without receipts?
2. Separate business and personal expenses
Use different bank accounts or cards to clearly track deductible business costs. Mixing your personal and business spending in one account is a recipe for confusion. So, get a separate bank account or card for your business—it makes tracking expenses so much cleaner.
This simple step not only saves time but also protects you if the IRS ever asks questions. Plus, it gives you a clearer picture of how your business is actually doing, which helps with smarter money decisions all year long.
You may like this: Types of Tax Credits for Small Businesses 2025
3. Track mileage and home office use
Mileage and home office deductions are gold but only if you’ve got records. For mileage, jot down your trips, where you went, and why it was business-related. Better yet, let an app do it for you in the background.
If you work from home, note which part of your space is used for work only, and keep a handle on related expenses like utilities or internet. These are details that often slip through the cracks... but they add up fast.
You may like this: What Is Self Employment Tax: Rates, Requirements, Deductions
4. Review deduction thresholds
Not every expense is deductible right away since some need to pass income-based thresholds first. For example, medical expenses only count if they go over 7.5% of your income.
Knowing these limits ahead of time helps you make smart moves, like bunching deductions in one year to cross the threshold. It’s not just about tracking—it’s about timing and strategy.
You may like this: Tax Loopholes for Small Businesses 2025
5. Consult a tax professional annually
Tax laws change often; a pro can help you maximize deductions and avoid errors. So, even if you feel confident filing on your own, talking to a tax pro once a year can make a big difference. They’re up to date on the latest rules, and they might spot deductions or credits you didn’t even know existed.
If your life or business changed in any way—new job, side hustle, big purchase—they’ll help you navigate it smartly. Think of them not just as a form-filler, but as someone helping you keep more of your hard-earned money.
You may like this: How to Beat Tax Extension Deadlines with Automation
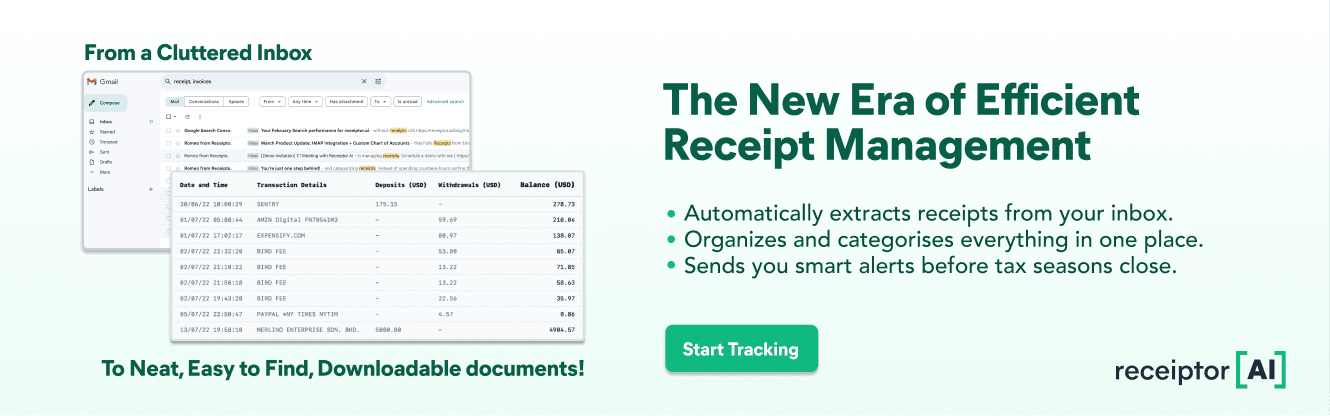
Claiming private school tuition as a tax deductible in the US? Here's how Receiptor AI can help you:
Keeping track of what’s deductible is one thing. Having proof ready when it counts? That’s where most people slip.
Receiptor AI helps you get organized — without the stress or spreadsheets. Here’s how:
1. Automatically collects your receipts from email and WhatsApp
No more digging through inboxes. Receiptor scans your connected accounts for receipts, invoices, and bills — even from months (or years) ago.
2. Categorizes expenses intelligently
Receiptor uses AI to understand your transactions' context. Whether it’s a premium for health insurance, a business lunch, or a home office chair — it tags everything correctly for your accountant (or the IRS).
3. Stores all deductible documents in one place
Forget the shoebox or random folders. All your documents live in one secure dashboard, searchable by merchant, category, or date.
4. Exports tax-ready reports
When tax season hits, you’re not starting from scratch. Export everything as a CSV, PDF, or ZIP — ready for TurboTax, your CPA, or your own filing.
5. Saves you hours (and money)
By catching missing deductions and automating your records, Receiptor helps you lower your tax bill and reclaim the time you’d spend chasing down receipts.
Quick FAQs
Can I deduct my private school tuition from my taxes?
No, tuition for private school is not deductible.
Can you claim your private school tuition deductible?
No, unless related to special needs and medical advice.
Do you get a tax refund for private school tuition?
Generally no, unless it qualifies under specific educational or medical exceptions.
Found this article helpful?
Read on to find out more about Receiptor AI.
